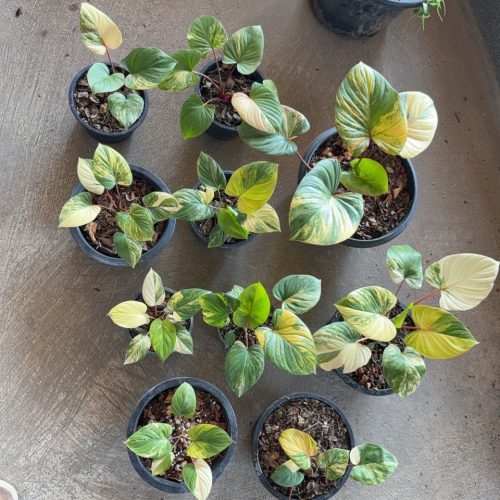
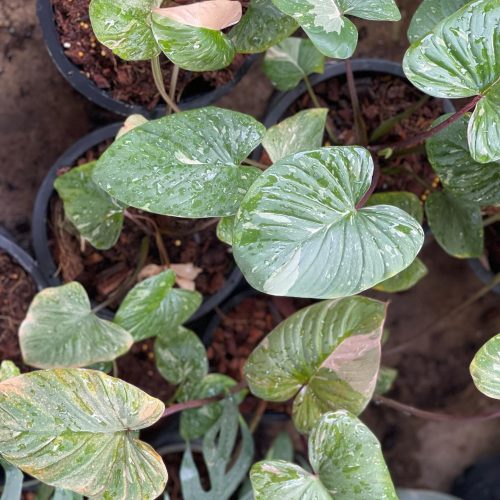
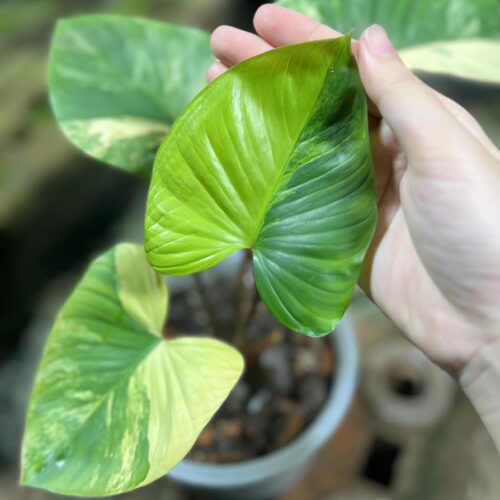
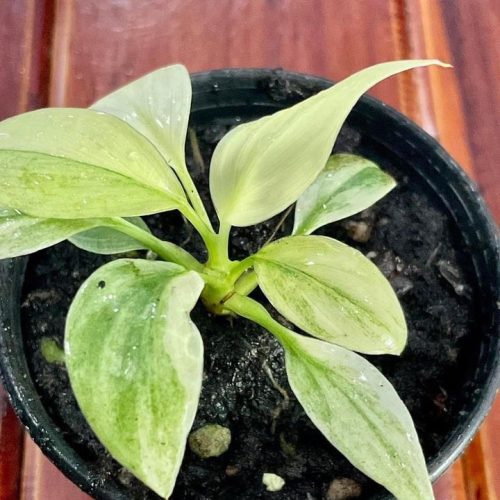
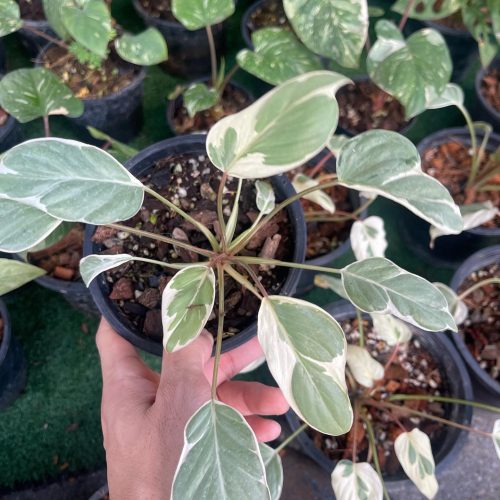
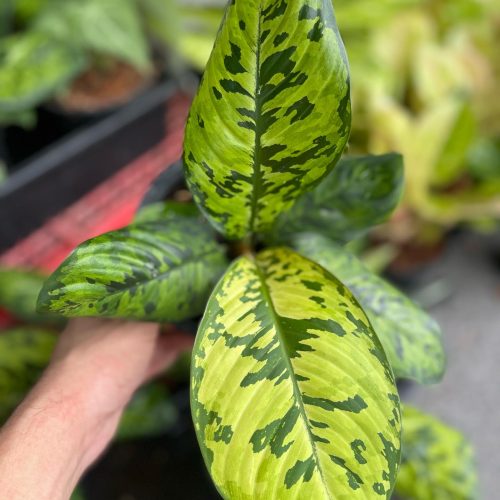
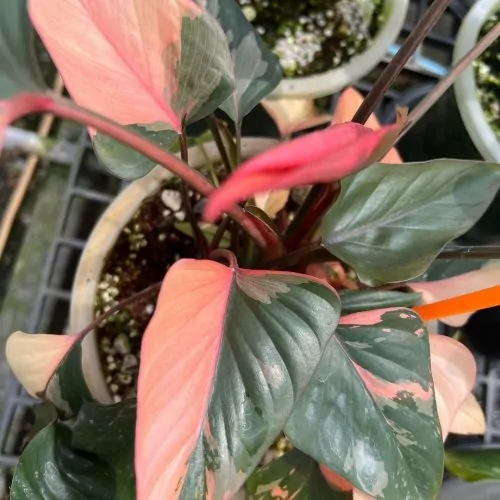
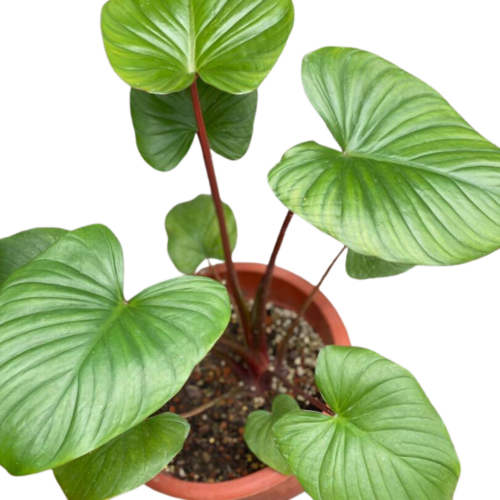
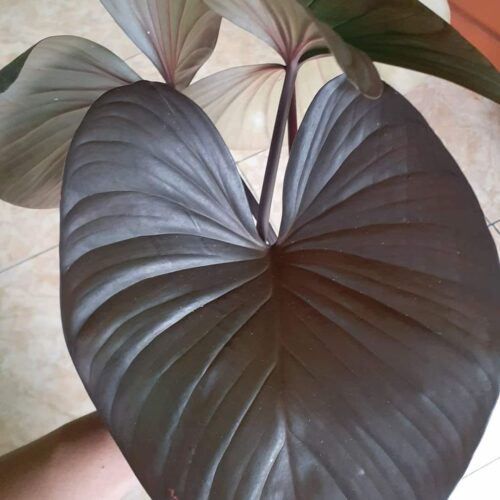
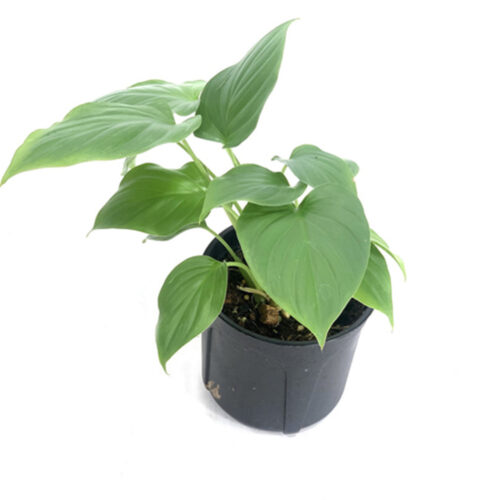
The Homalomena is a stunning tropical plant known for its attractive foliage and easy care. Breeding this plant can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to propagate new plants and expand your collection. Follow these five simple steps to successfully breed your Homalomena.
Introduction
The Homalomena is a member of the aroid plant family, which includes popular varieties like Philodendron, Monstera, and Anthurium. Native to the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, this plant is prized for its lush, heart-shaped leaves and vibrant colors. Similar to Aglaonema and Epipremnum, the Homalomena is not only beautiful but also relatively easy to breed with the right method.
Selecting Parent Plants
Choosing healthy, mature parent plants from which to collect propagation material is the first key step. Consider the following when selecting candidates:
Age and Size
Select established plants that are at least 2-3 years old. Older, larger plants tend to propagate more readily. The parent plants should have several mature leaves and an extensive root system to support new growth.
Desired Characteristics
Choose parent plants that exhibit desirable traits like lush foliage, vivid leaf patterns, unique textures that you wish to replicate in new plants. Observe them over time and propagate from healthy, vigorous specimens. Avoid selecting diseased or infected plants.
Cross-pollinating two plants with complementary qualities can yield interesting new varieties too.
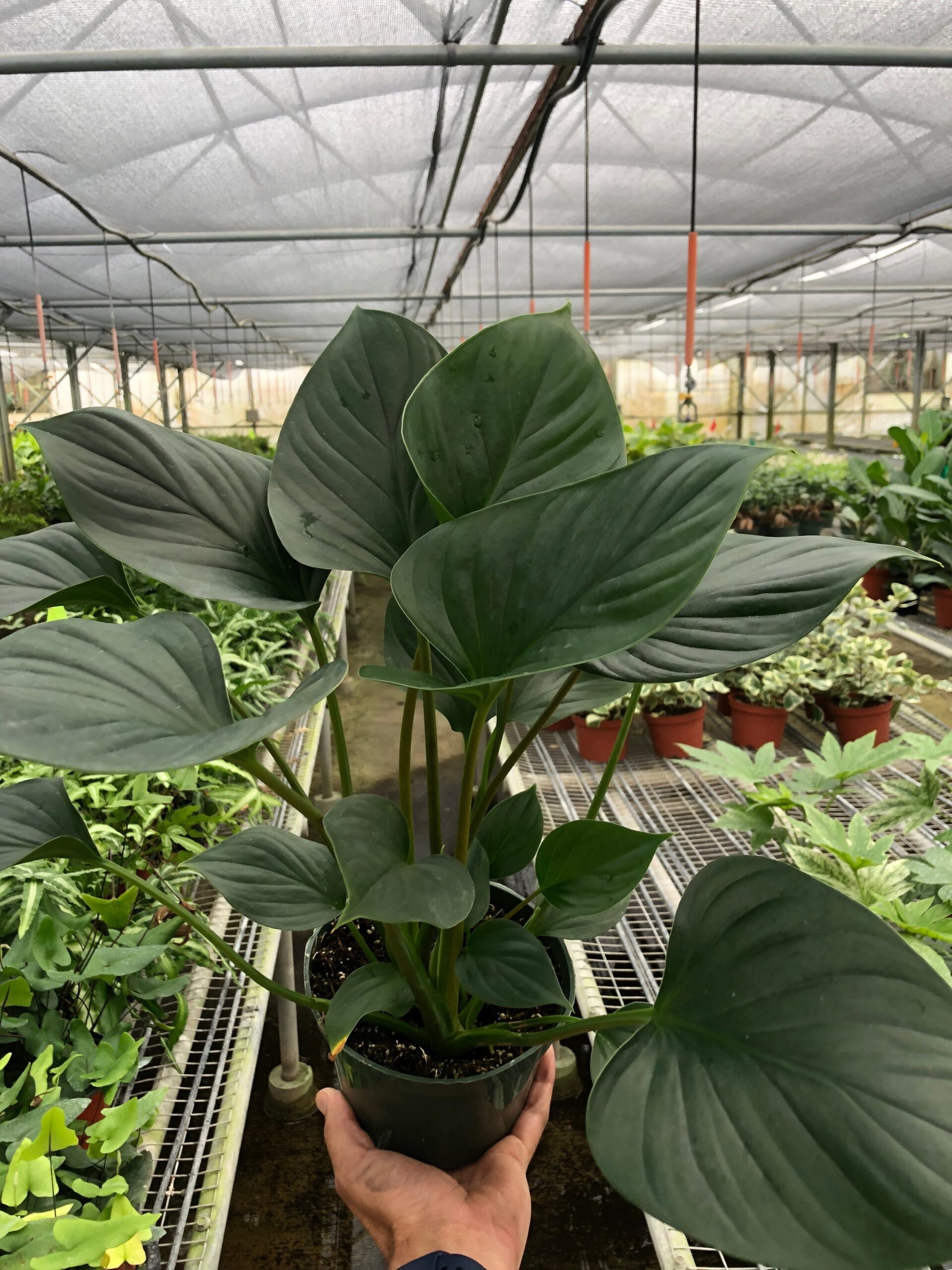

Gathering Propagation Materials
Once suitable parents are chosen, the next step is carefully collecting propagation materials:
Plant Divisions
These are small connected sections of the parent plant containing roots, stems, and leaves which can grow into independent plants when separated. For homalomena, new offsets that form adjacent to mature specimens often make good candidates for dividing.
Stem Cuttings
Stem cuttings involve snipping off sections of stem, then rooting them in water or media to generate a new plant. Take 5-6 inch stem cuttings from the healthiest parts of the plant, ideally just below a leaf node which can form new roots.
Seeds (for sexual reproduction)
To generate entirely new genetic offspring, collect ripe seed pods once they form on flowers, then extract and store the seeds in a dry paper envelope until ready to sow.
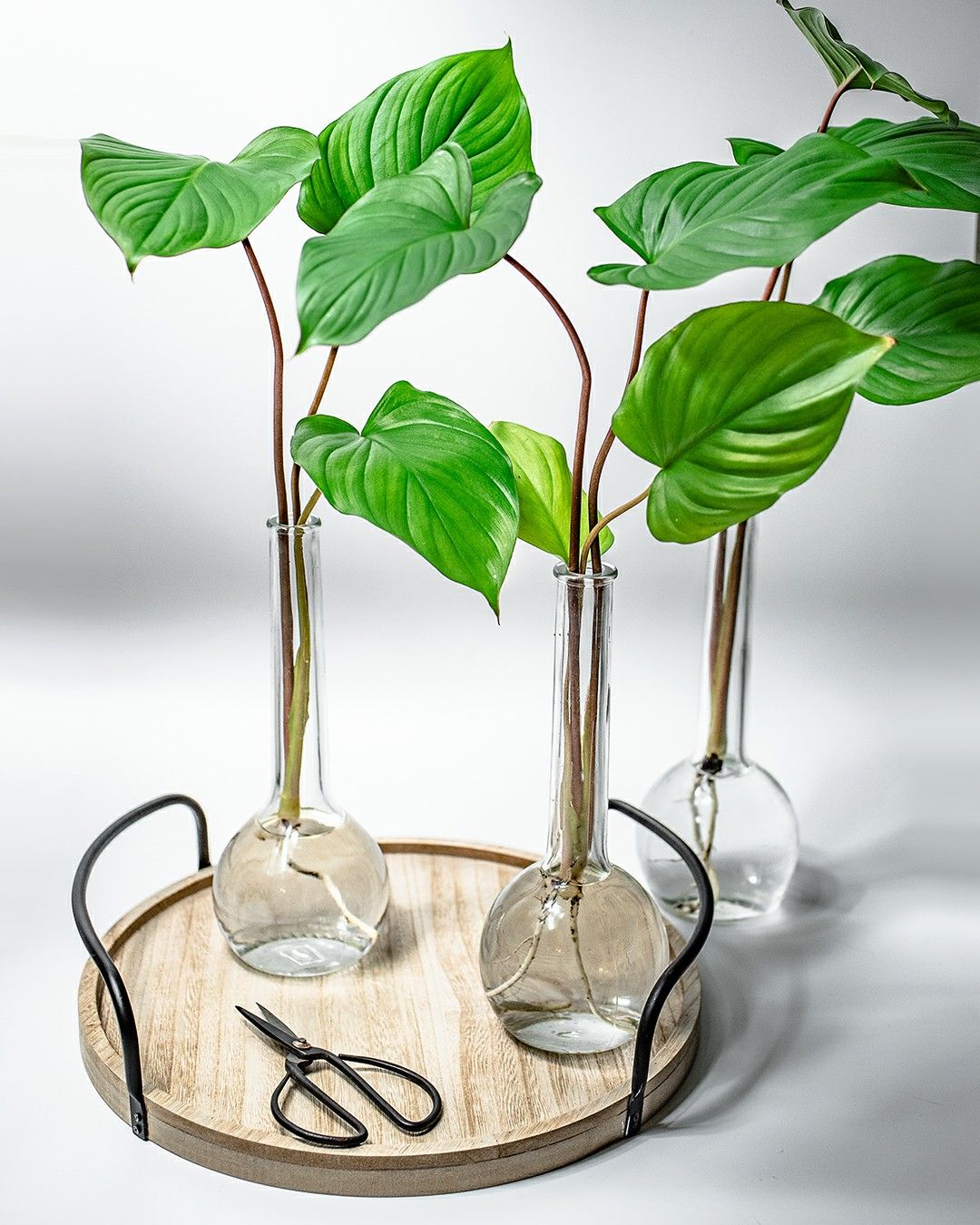

List of the most sought after Homalomena species in 2023
Propagation of Cuttings
Once high quality propagation materials are gathered, the process of regenerating new plants begins:
Rooting Medium
Moisten sphagnum moss and perlite to create an airy yet moist rooting medium. The mixture should not be too wet or compact. Gently place each cutting or division into the mix, making sure some nodes are buried.
Environmental Conditions
Maintain high ambient humidity around 80-90% using domes or bags to prevent moisture loss from new cuttings until they root. Keep rooting trays in filtered light. Warm temperatures of 70-80°F will encourage faster root establishment.
Ongoing Care
Check cuttings every few days. Lightly mist to restore moisture if the medium starts to dry out before sufficient roots form. Transplant into pots once new growth is evident, then transition to higher light and normal watering schedule.
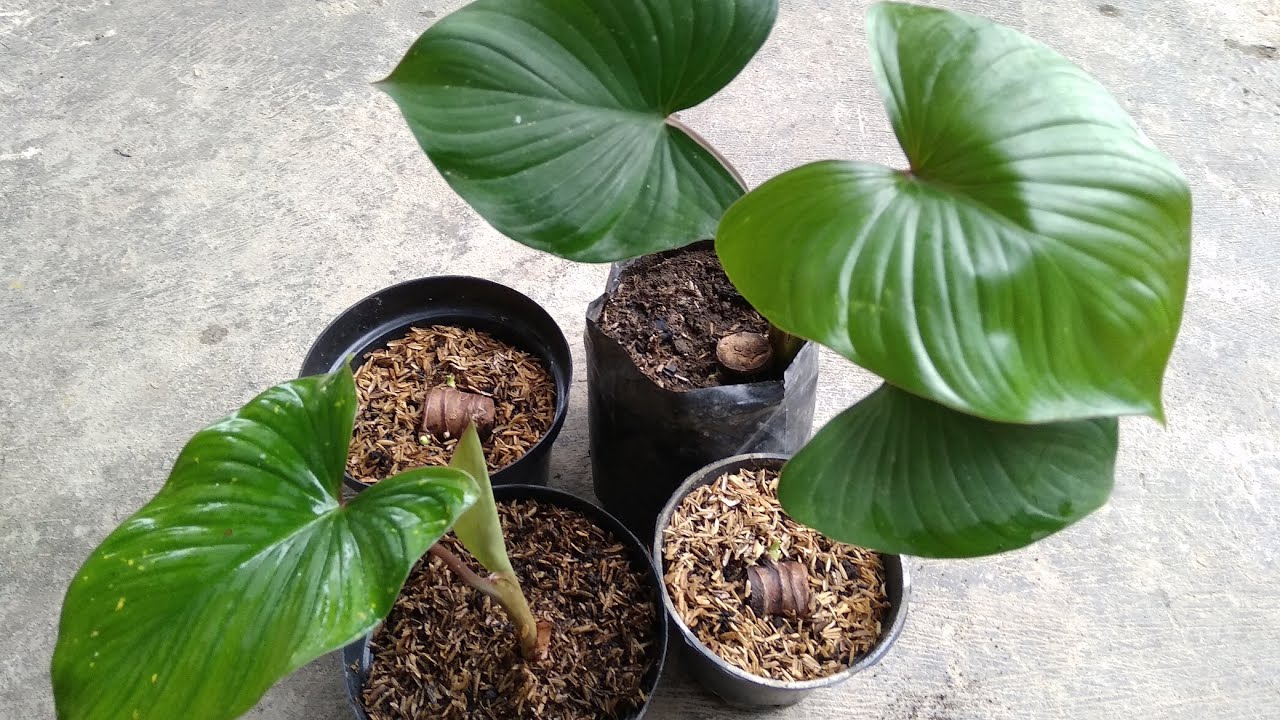

Benefits of Breeding Homalomena
Breeding your Homalomena allows you to expand your collection and share this beautiful plant with friends and family. Additionally, breeding helps maintain the health of the parent plants by encouraging new growth. Similar benefits can be enjoyed when breeding other aroid plants like Philodendron and Monstera.
Sowing Seeds
For seeds gathered via sexual reproduction, the process involves:
Preparing Containers
Fill small seedling pots or flats with a lightweight, nutrient seed starting mix. Moisten the mix, then sow 2-3 seeds just below the surface per container, spaced apart.
Germination Conditions
Cover containers with plastic wrap or dome lids to retain moisture, providing high humidity. Place in bright, indirect light around 70-75°F to stimulate germination.
Ongoing Care
Once sprouted, remove coverings gradually over a week to acclimate seedlings. Thin down to the strongest seedling per pot. Maintain warm, humid conditions with adequate airflow and light while they establish. Fertilize lightly with half strength liquid fertilizer once established.
Transferring & Continued Growth
As new young plants from cuttings or seeds grow larger with developed roots and leaves, they can be shifted into individual pots:

Potting Mix
Repot new plants into pots with drainage holes, using a rich, loose potting soil amended with orchid bark, perlite and compost. This will encourage healthy root and foliage growth as they continue to mature.
Transition Conditions
Gradually transition propagated plants to normal indoor conditions over a period of 2-4 weeks. Slowly increase light exposure, ease up on humidity, and water only when soil begins to dry out. Fertilize monthly during growing season.
Ongoing Maintenance
Monitor new plants closely as they establish under normal conditions. Stake or trellis larger species prone to toppling over. Divide congested clumps every few years. Identify and address any pest or disease issues promptly. Propagated plants will exhibit unique new qualities.
Homalomena species are the most sought after by aroid plant lovers
Conclusion
Propagating homalomena by plant division, stem cuttings, or seeds can perpetuate treasured specimens or even produce new varieties expressing novel traits. Following simple steps for selection, material gathering, rooting, and gradual transition to finished plants allows gardeners to sustain these delightful aroids. Incorporate the techniques here to expand any homalomena collection through breeding.
FAQ
- How do I propagate homalomena plants?
- To propagate homalomena, you can use methods like division, stem cuttings, or leaf cuttings. Each method has its own requirements and steps, so be sure to follow the appropriate one for your plant.
- When is the best time to propagate homalomena?
- The best time to propagate homalomena is during its active growing season, which is typically in the spring or early summer. This is when the plant is more likely to root and grow successfully.
- What are the key factors for successful homalomena propagation?
- Successful propagation of homalomena requires factors such as the right soil mix, appropriate humidity levels, and optimal temperature conditions. Proper care and attention to these factors will increase your chances of success.
- Can I propagate homalomena in water?
- Yes, you can propagate some homalomena varieties in water, particularly from stem cuttings. Place the cutting in a container of clean water and wait for roots to develop before transplanting it into soil.
- How long does it take for propagated homalomena to grow into mature plants?
- The time it takes for propagated homalomena to grow into mature plants can vary depending on the propagation method and environmental conditions. In general, it may take several months to a year or more for them to reach maturity and display their full foliage.
See more Caring for an Homalomena – 5 Important Things to Keep in Mind


























![12x Monstera Borsigiana Albo half leaves variegata [3-4 leaves]](https://greenboog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Monstera-Borsigiana-Albo-half-leaves-variegata-1-500x500.jpg)







![10 Pots x Monstera Aurea Variegated / Mix Aurea tri color 3-4 leaves [well variegated]](https://greenboog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Monstera-Aurea-Tri-color-500x500.jpg)




![[SALE] 10 Pots x Monstera Aurea Variegated 3-6 leaves [Medium size]](https://greenboog.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Monstera-Aurea-variegated-4-6-leafs-500x482.jpg)